Filter by
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
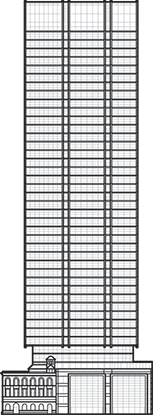
Lumiere
Lumiere Residences, Tower A
Building
Completed
2007
Residential
All-Concrete
152 m / 499 ft
47
8
447
448
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Construction Start
Completed
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Usually takes on the balance of the architectural effort not executed by the "Design Architect," typically responsible for the construction documents, conforming to local codes, etc. May often be referred to as "Executive," "Associate," or "Local" Architect, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Architect of Record" exclusively.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Usually takes on the balance of the architectural effort not executed by the "Design Architect," typically responsible for the construction documents, conforming to local codes, etc. May often be referred to as "Executive," "Associate," or "Local" Architect, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Architect of Record" exclusively.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
2017 CTBUH Awards
9 November 2008 - Event
9 November 2008 - Event

30 May 2018 | Sydney
Perhaps only a few could have predicted the degree to which Lumiere Residences would so thoroughly encapsulate an Australian sensibility toward vertical architecture when it...
Lumière Residences is the main residential tower within the Regent Place mixed-use development at the heart of Sydney. Eight slender volumes supported by a central core provide a diverse village of 456 apartments floating above a five-level podium, which reflects the scale of adjacent historic buildings and engages with the city center through mixed retail, commercial and leisure spaces. As a point of reference for the city skyline, the tower becomes increasingly transparent as it rises into the sky, its floating effect accentuated by black glazed necking of the façade above the podium, where lush landscaped terraces mingle visually with street tree-tops.
Projecting fins to the edge of each sleek glass and metal volume enhance their strong vertical form, while deep recesses into the heart of the tower allow daylight, cross ventilation and views from each lobby. Balconies integrated within the metal and glass façade create loggia for year-round use while preserving a seamless appearance in harmony with neighboring buildings. Internal folding screen doors, combined with sliding and awning windows, adapt to changes in climate and preferred use, while lower dark glazing maximizes privacy and outlook. The utilization of double glazing and water-efficient fixtures contributes to this sustainable strategy.
2017 CTBUH Awards
15 November 2008
During his week in Australia Executive Director Antony Wood had a chance to visit many of the tall buildings, including Riverside Center, Aurora Place, and Governor Philip Tower.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy