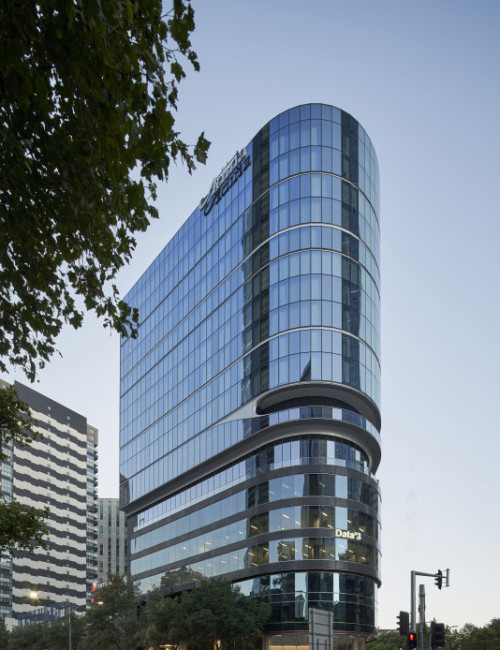
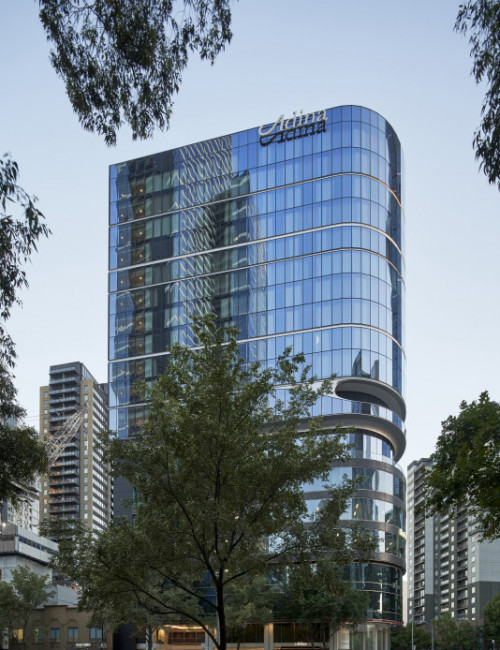
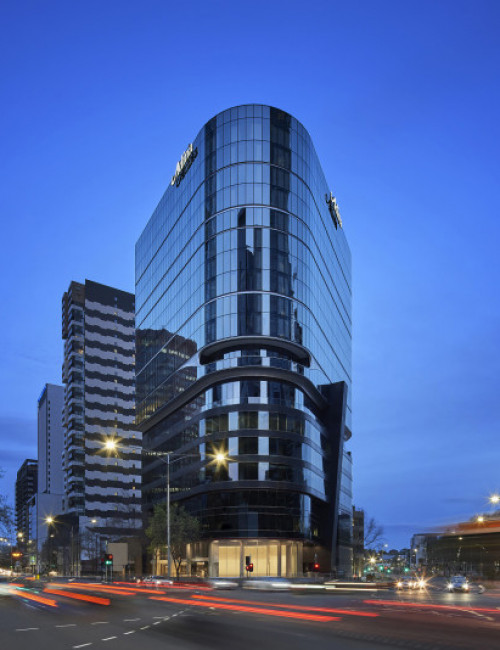
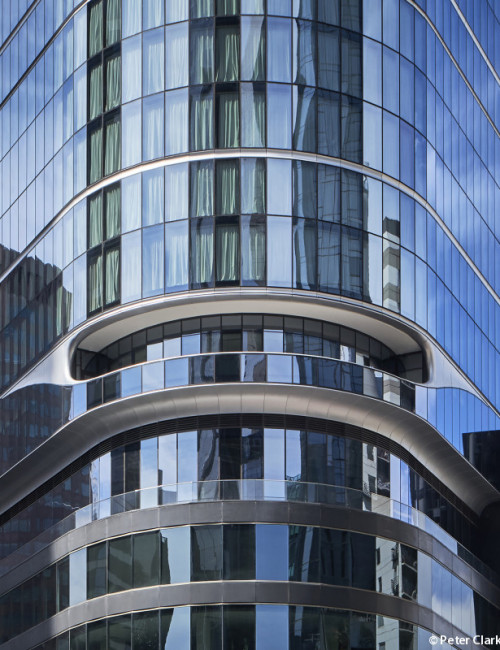
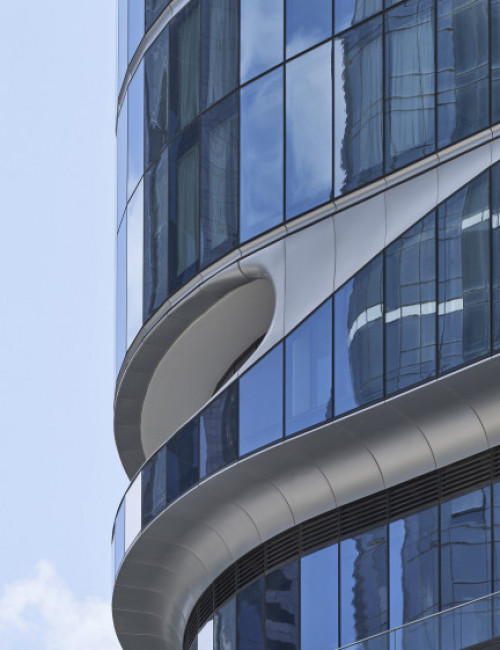
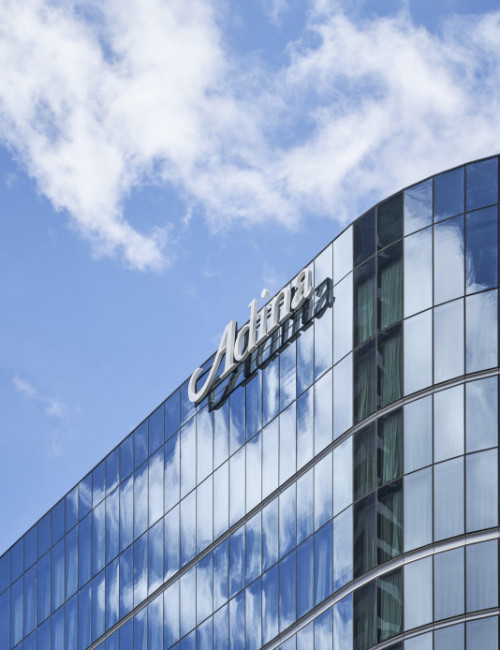
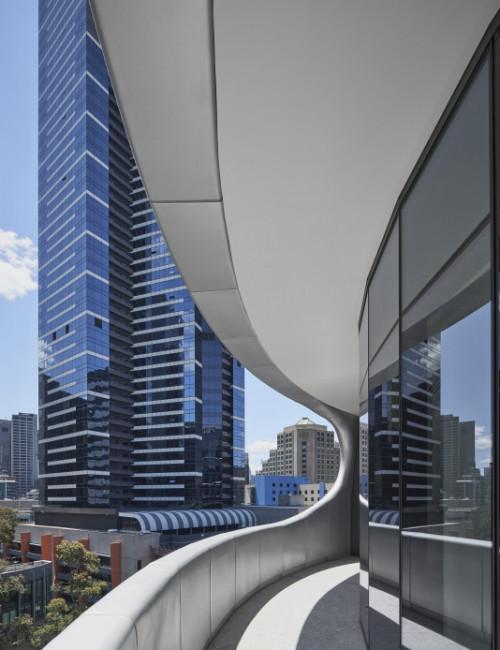
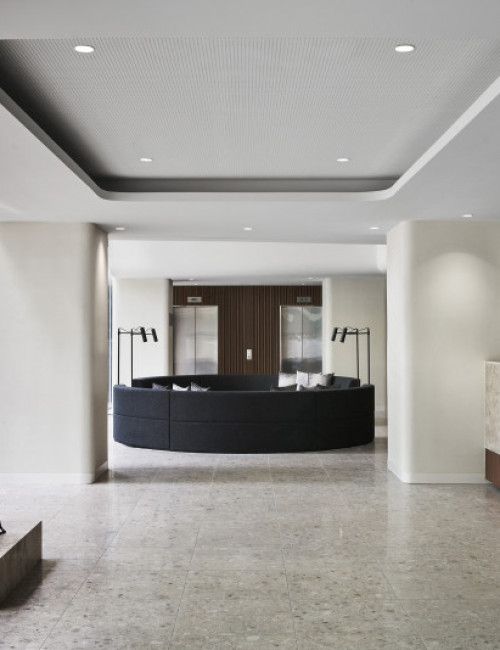
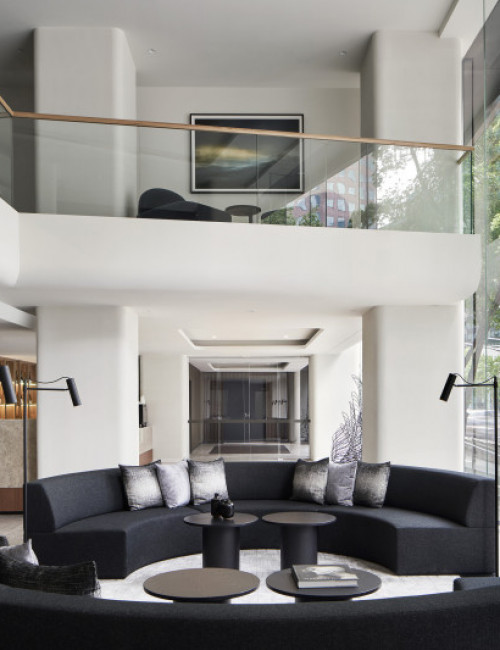
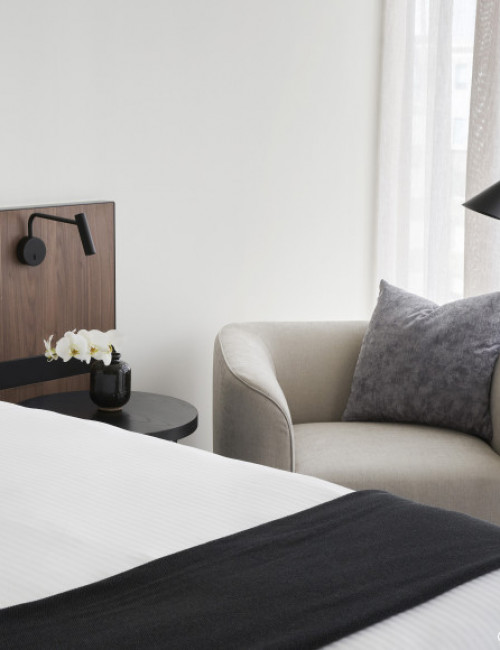
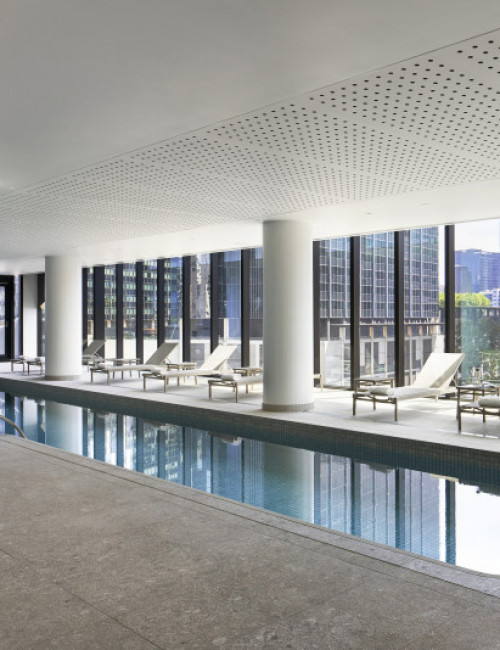
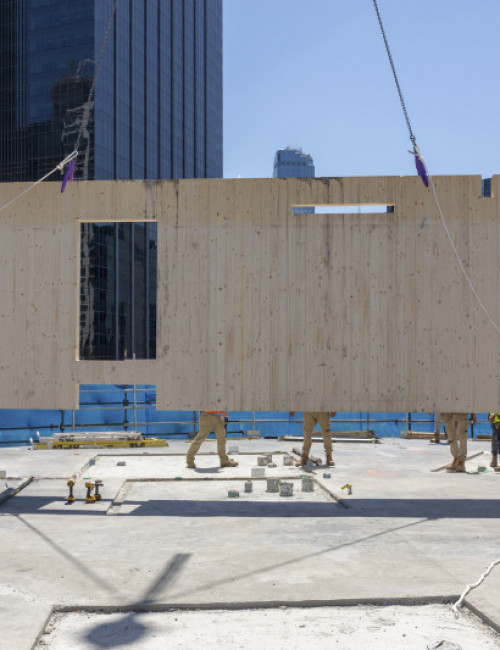
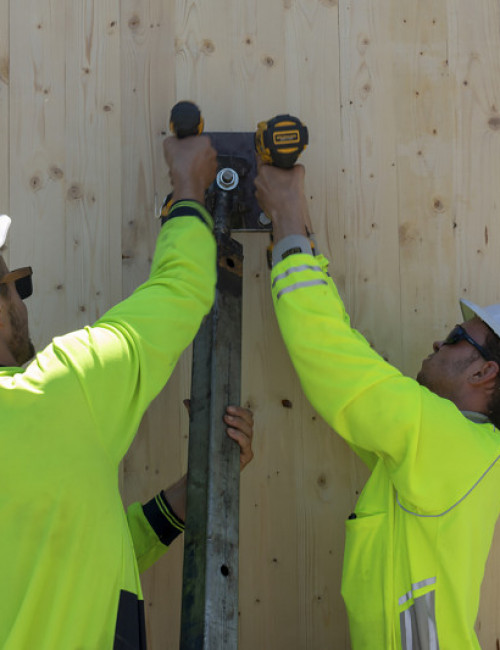
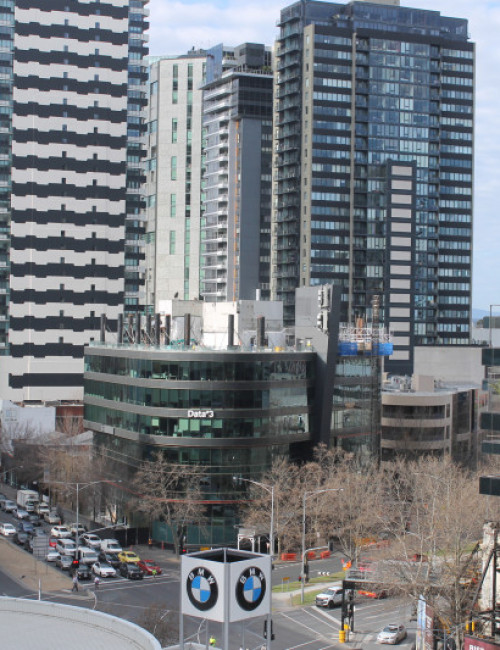
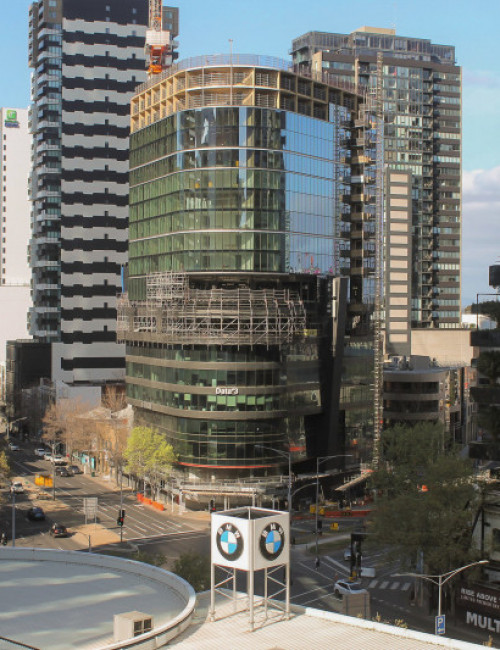
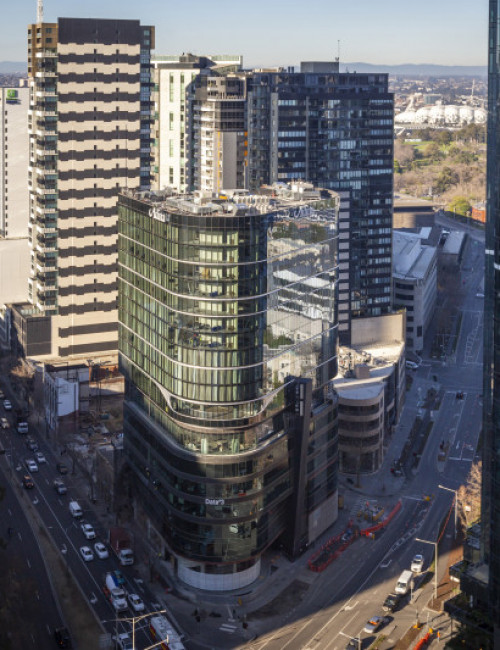
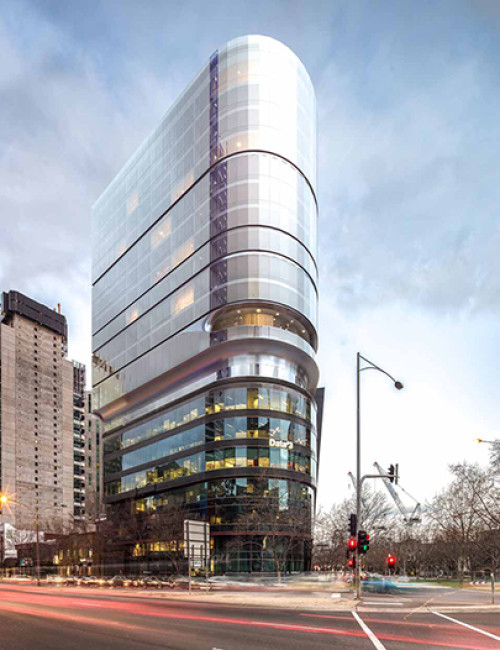
55 Southbank
Melbourne
Official Name
55 Southbank
Other Names
Adina Apartment Hotel Melbourne Southbank, 99 City Road
Type
Building
Status
Completed
Completion
2020
Country
City
Address
Function
A mixed-use tall building contains two or more functions (or uses), where each of the functions occupy a significant proportion of the tower's total space. Support areas such as car parks and mechanical plant space do not constitute mixed-use functions. Functions are denoted on CTBUH "Tallest Building" lists in descending order, e.g., "hotel/office" indicates hotel function above office function.
Hotel / Office
Structural Material
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from steel. Note that a building of steel construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of steel beams is still considered an “all-steel” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
All-Concrete
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from concrete which has been cast in place and utilizes steel reinforcement bars and/or steel reinforced concrete which has been precast as individual components and assembled together on-site.
All-Timber
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from timber. An all-timber structure may include the use of localized non-timber connections between timber elements. Note that a building of timber construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of timber beams is still considered an “all-timber” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
Mixed-Structure
Utilizes distinct systems (e.g. all-steel, all-concrete, all-timber), one on top of the other. For example, a Steel Over Concrete indicates an all-steel structural system located on top of an all-concrete structural system, with the opposite true of Concrete Over Steel.
Composite
A combination of materials (e.g. steel, concrete, timber) are used together in the main structural elements. Examples include buildings which utilize: steel columns with a floor system of reinforced concrete beams; a steel frame system with a concrete core; concrete-encased steel columns; concrete-filled steel tubes; etc. Where known, the CTBUH database breaks out the materials used within a composite building’s primary structural elements.
Steel-Timber Composite Over Concrete
Height
69.7 m / 229 ft
Floors Above Ground
19
Floors Below Ground
1
# of Hotel Rooms
220
# of Elevators
3
Tower GFA
27,000 m² / 290,626 ft²
Structural Details:
Floors 1 – 9
Floors 10 – 19
Construction Schedule
Proposed
Construction Start
Completed
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Project Manager
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
Other Consultant
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Owner/Developer
Hume Partners Property
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Vistek Engineers; WSP Group
MEP Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Scientific Fire Services Pty Ltd
Project Manager
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
Contractor
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Atelier Projects
Other Consultant
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Marshall Day Acoustics
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
TFE Hotels
MEL Consultants Pty Ltd
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Hyne & Son
KLH Australia; XLam
CTBUH Awards & Distinctions
Renovation Award 2022 Winner
2022 CTBUH Awards
CTBUH Initiatives
Tall Timber: A Global Audit
26 June 2017 - CTBUH Research
Videos

01 October 2020 | Melbourne
Timber Rising | Philip Vivian
Designing Tall Mass Timber Office Buildings: 25 King, Brisbane, & 55 Southbank, Melbourne
Research
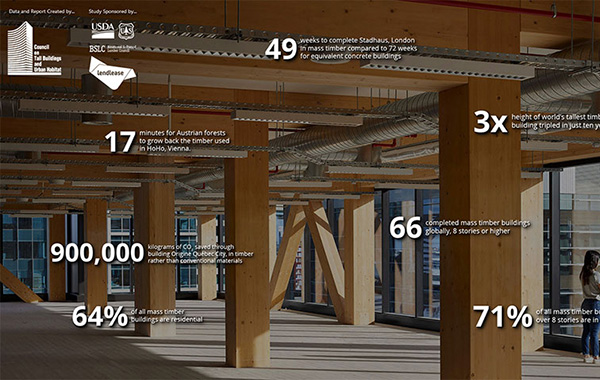
23 May 2022
Interactive Study - The State of Tall Timber: A Global Audit
CTBUH Research
This data study represents the significant recent momentum of the mass-timber movement worldwide. There are now 139 mass timber buildings around the world of eight...
CTBUH Awards & Distinctions
Renovation Award 2022 Winner
2022 CTBUH Awards
Quick Facts
- 55 Southbank was an existing concrete building of 10 floors, including the above-grade parking levels and was originally intended for six additional floors of occupiable space. By utilizing cross-laminated timber (CLT) for the vertical completion, four additional floors can be accommodated due to the lighter weight of the wood framing.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy






























