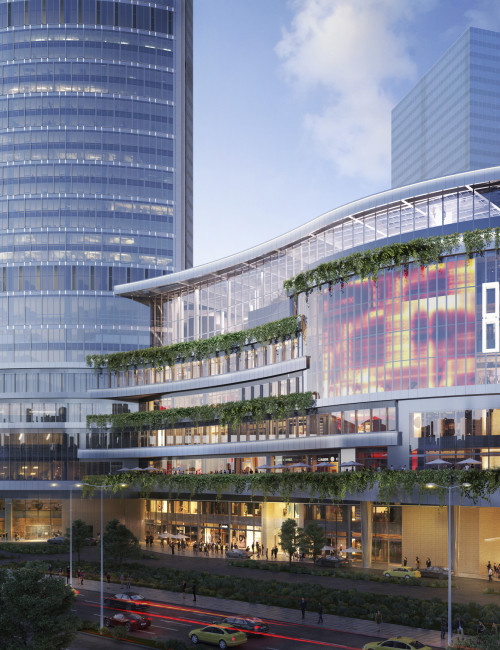
International Land-Sea Center
Chongqing
Note: As this project is architecturally topped out, the data is based on the most reliable information currently available. This data is thus subject to change until the building has completed and all information can be confirmed and ratified by the CTBUH.
- CTBUH Drawing
- Facts
-
Metrics
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
To Tip:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest point of the building, irrespective of material or function of the highest element (i.e., including antennae, flagpoles, signage and other functional-technical equipment).Architectural:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the architectural top of the building, including spires, but not including antennae, signage, flag poles or other functional-technical equipment. This measurement is the most widely utilized and is employed to define the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat (CTBUH) rankings of the "World's Tallest Buildings."Occupied:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest occupied floor within the building.Above Ground
The number of floors above ground should include the ground floor level and be the number of main floors above ground, including any significant mezzanine floors and major mechanical plant floors. Mechanical mezzanines should not be included if they have a significantly smaller floor area than the major floors below. Similarly, mechanical penthouses or plant rooms protruding above the general roof area should not be counted. Note: CTBUH floor counts may differ from published accounts, as it is common in some regions of the world for certain floor levels not to be included (e.g., the level 4, 14, 24, etc. in Hong Kong).Below Ground
The number of floors below ground should include all major floors located below the ground floor level.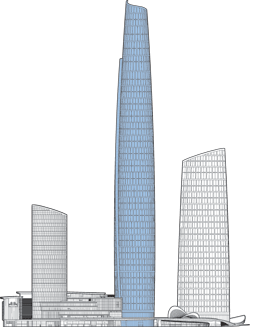
Official Name
International Land-Sea Center
Other Names
Chongqing International Trade and Commerce Center 1, Chongqing 100, Vanke Center,Jialing Fanying Tower 1
Name of Complex
Type
Building
Status
Architecturally Topped Out
Expected Completion
2024
Country
City
Address
Function
A mixed-use tall building contains two or more functions (or uses), where each of the functions occupy a significant proportion of the tower's total space. Support areas such as car parks and mechanical plant space do not constitute mixed-use functions. Functions are denoted on CTBUH "Tallest Building" lists in descending order, e.g., "hotel/office" indicates hotel function above office function.
Hotel / Office
Structural Material
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from steel. Note that a building of steel construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of steel beams is still considered an “all-steel” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
All-Concrete
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from concrete which has been cast in place and utilizes steel reinforcement bars and/or steel reinforced concrete which has been precast as individual components and assembled together on-site.
All-Timber
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from timber. An all-timber structure may include the use of localized non-timber connections between timber elements. Note that a building of timber construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of timber beams is still considered an “all-timber” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
Mixed-Structure
Utilizes distinct systems (e.g. all-steel, all-concrete, all-timber), one on top of the other. For example, a Steel Over Concrete indicates an all-steel structural system located on top of an all-concrete structural system, with the opposite true of Concrete Over Steel.
Composite
A combination of materials (e.g. steel, concrete, timber) are used together in the main structural elements. Examples include buildings which utilize: steel columns with a floor system of reinforced concrete beams; a steel frame system with a concrete core; concrete-encased steel columns; concrete-filled steel tubes; etc. Where known, the CTBUH database breaks out the materials used within a composite building’s primary structural elements.
Concrete-Steel Composite
Energy Label
LEED Gold BD+C: Core and Shell
Official Website
Height
458.2 m / 1,503 ft
Floors Above Ground
98
Floors Below Ground
4
# of Parking Spaces
815
# of Elevators
59
Top Elevator Speed
7 m/s
Tower GFA
248,470 m² / 2,674,509 ft²
Construction Schedule
Proposed
Construction Start
Completed
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
MEP Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Other Consultant
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Owner
China Vanke Co.,Ltd
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Chongqing Architectural Design Institute Co., LTD.; Kohn Pedersen Fox Associates
Usually takes on the balance of the architectural effort not executed by the "Design Architect," typically responsible for the construction documents, conforming to local codes, etc. May often be referred to as "Executive," "Associate," or "Local" Architect, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Architect of Record" exclusively.
P & T Group
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
MEP Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Contractor
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
China Construction Third Engineering Bureau Co., Ltd.
Other Consultant
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Design Land Collaborative
duttonBRAY Design Limited
NOVA Fluid Mechanics; Cermak Peterka Petersen (CPP), Inc.
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Jangho Group Co., Ltd.
Favelle Favco Group
Jotun
China Construction Steel Structure Corporation
CTBUH Initiatives
Top Company Rankings: The World’s 100 Tallest Buildings
13 October 2016 - CTBUH Research
Global News

20 June 2022
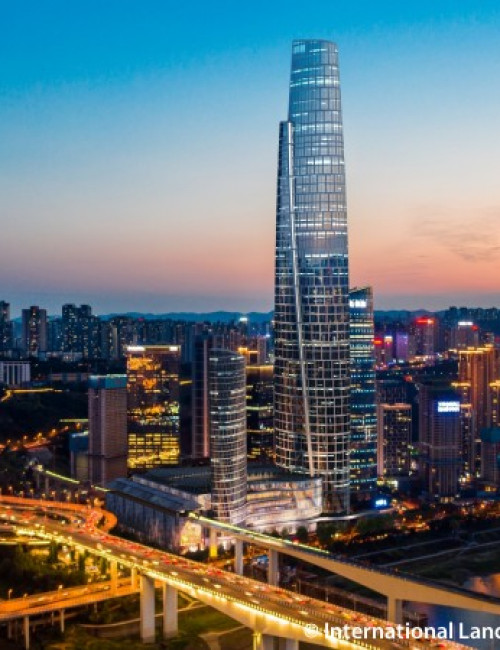
Chongqing Skyscraper Tops Out at 458.2 Meters
The International Land-Sea Center, a 458.2-meter-tall skyscraper had its roof sealed on Saturday, 18 June 2022. The total length of the building’s butt welds is over...
About International Land-Sea Center
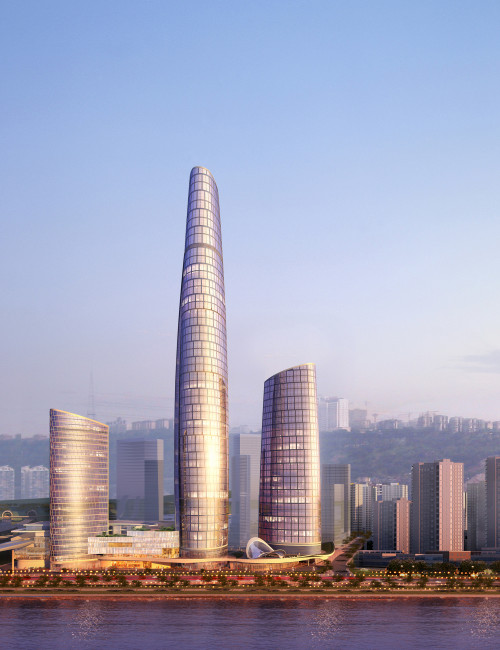
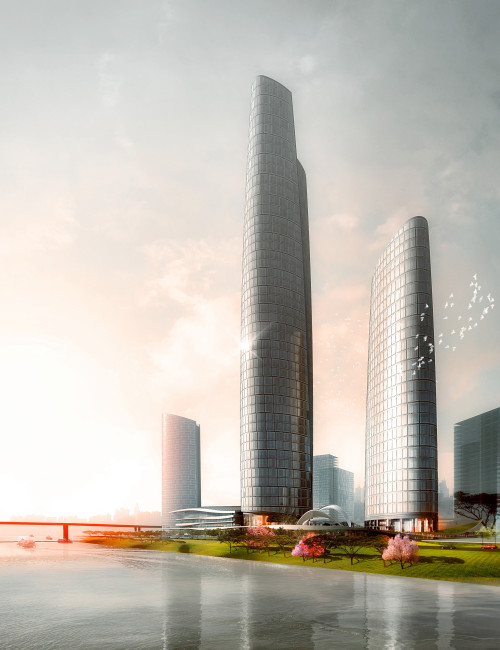
As a centerpiece of the 3.6-million-square-meter Chongqing Tian Di Master Plan, a major redevelopment of the downtown core area, the Chongqing International Commerce Center will provide a nexus of activity, bringing people together for both work and leisure. Informed by curvilinear geometry, the complex’s light and graceful form is clearly expressed in the simple configuration of the International Land-Sea Center, the tallest tower on site.
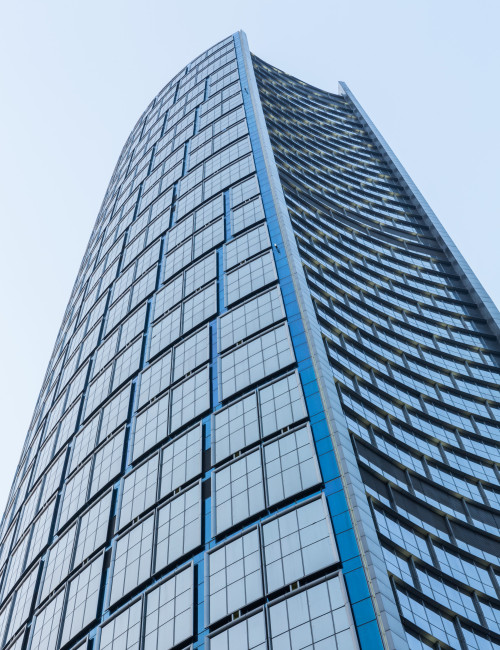
The architectural language used to realize the building acknowledges the city’s ancient cultural, social, and economic origins; the central and local government’s visionary “314” Overall Plan; and Chongqing’s geographic location. The sail design brings to life the commercial junk ships that long navigated the Yangtze and Jialing Rivers, Chongqing’s primary routes to the outside world. The main tower’s two overlapping sail forms generate an oval in plan. The sail form is also evident in the wavelike design of the podium roof. The exterior wall design aims to instill a sense of movement and lightness. Consisting of glass, the façade defines the curving form of the tower, sloping inwards as they rise and adding to the organic feel of the structure. This form also helps to minimize light contamination, as the light hitting the exterior surfaces will be dispersed rather than concentrated.
International Land-Sea Center’s façade pattern is designed to evoke Chongqing’s image as the city of “double happiness,” as window units are organized in groups of two. This allusion seamlessly unites the architectural ambition of the urban renewal project with the city’s plans to incorporate the strengths of its past into the potential of its future. The duality expressed in all three of the towers in the complex is meant to harmonize with these aspirations.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy














