Height rank
J.W. Marriott and The Upper House
Hong Kong
- CTBUH Drawing
- Facts
-
Metrics
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
To Tip:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest point of the building, irrespective of material or function of the highest element (i.e., including antennae, flagpoles, signage and other functional-technical equipment).Architectural:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the architectural top of the building, including spires, but not including antennae, signage, flag poles or other functional-technical equipment. This measurement is the most widely utilized and is employed to define the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat (CTBUH) rankings of the "World's Tallest Buildings."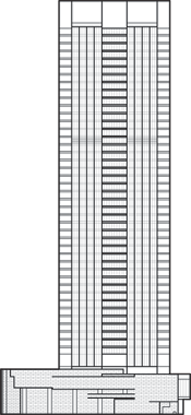
Above Ground
The number of floors above ground should include the ground floor level and be the number of main floors above ground, including any significant mezzanine floors and major mechanical plant floors. Mechanical mezzanines should not be included if they have a significantly smaller floor area than the major floors below. Similarly, mechanical penthouses or plant rooms protruding above the general roof area should not be counted. Note: CTBUH floor counts may differ from published accounts, as it is common in some regions of the world for certain floor levels not to be included (e.g., the level 4, 14, 24, etc. in Hong Kong).Official Name
J.W. Marriott and The Upper House
Name of Complex
Type
Building
Status
Completed
Completion
1988
Country
City
Address
Function
A mixed-use tall building contains two or more functions (or uses), where each of the functions occupy a significant proportion of the tower's total space. Support areas such as car parks and mechanical plant space do not constitute mixed-use functions. Functions are denoted on CTBUH "Tallest Building" lists in descending order, e.g., "hotel/office" indicates hotel function above office function.
Hotel
Height
164.5 m / 540 ft
Floors Above Ground
50
# of Hotel Rooms
719
Rankings
-
By function
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Construction Schedule
Construction Start
Completed
Retrofit End
Owner/Developer
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Contractor
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Owner/Developer
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Wong & Ouyang
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Contractor
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Research

17 October 2016
Shifting Urban Gravity, from “Central” To “Core” Business Districts
Tim Balckburn, Swire Properties
In the age of the multi-million inhabitant city, the traditional concept of a single Central Business District (CBD) is becoming increasingly unrealistic. As we are...
About J.W. Marriott and The Upper House
Constructed at the base of a hill sloping upward from Victoria Harbour, the Pacific Place Complex sits adjacent to Hong Kong Park, both of which were constructed on the site of the Victoria Barracks operated by the British Military. While the western portion of the barracks became public a green space interspersed with a collection of preserved low-rise structures from Hong Kong’s colonial era, the eastern portion gave way to the Pacific Place development. After the land was transferred from the Government of Hong Kong in the mid 1980’s, construction began quickly with Phase 1 opening in 1988.
Phase 1 included One Pacific Place as the as the J.W. Marriott and The Upper House which was originally constructed as a mixed use residential and hotel tower with 140 serviced apartments above 607 hotel rooms. As part of a later interior retrofit, the uppermost floors were converted from residential into the suites of the 117 key Upper House Hotel which opened in 2009. Combined with the JW Marriott hotel below, there are presently 719 rooms as well as a handful of restaurants spread throughout the tower.
The tower is perched on a hillside podium comprised of the three story Pacific Place shopping mall and a landscaped rooftop serving a courtyard between the towers of the complex as well as the publicly accessible street linking the main entrances of each building. The J.W. Marriott and The Upper House features a glass façade composed of triangular window bays maximizing views of the surrounding harbour, hilltops and skyline which has grown up around it since completion.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy












