Victoria Tower
Stockholm
- CTBUH Drawing
- Facts
-
Metrics
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
To Tip:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest point of the building, irrespective of material or function of the highest element (i.e., including antennae, flagpoles, signage and other functional-technical equipment).Architectural:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the architectural top of the building, including spires, but not including antennae, signage, flag poles or other functional-technical equipment. This measurement is the most widely utilized and is employed to define the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat (CTBUH) rankings of the "World's Tallest Buildings."Above Ground
The number of floors above ground should include the ground floor level and be the number of main floors above ground, including any significant mezzanine floors and major mechanical plant floors. Mechanical mezzanines should not be included if they have a significantly smaller floor area than the major floors below. Similarly, mechanical penthouses or plant rooms protruding above the general roof area should not be counted. Note: CTBUH floor counts may differ from published accounts, as it is common in some regions of the world for certain floor levels not to be included (e.g., the level 4, 14, 24, etc. in Hong Kong).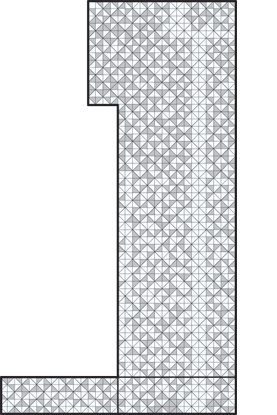
Official Name
Victoria Tower
Other Names
Scandic Hotel Kista
Type
Building
Status
Completed
Completion
2011
Country
City
Address
Function
A mixed-use tall building contains two or more functions (or uses), where each of the functions occupy a significant proportion of the tower's total space. Support areas such as car parks and mechanical plant space do not constitute mixed-use functions. Functions are denoted on CTBUH "Tallest Building" lists in descending order, e.g., "hotel/office" indicates hotel function above office function.
Hotel / Office
Structural Material
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from steel. Note that a building of steel construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of steel beams is still considered an “all-steel” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
All-Concrete
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from concrete which has been cast in place and utilizes steel reinforcement bars and/or steel reinforced concrete which has been precast as individual components and assembled together on-site.
All-Timber
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from timber. An all-timber structure may include the use of localized non-timber connections between timber elements. Note that a building of timber construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of timber beams is still considered an “all-timber” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
Mixed-Structure
Utilizes distinct systems (e.g. all-steel, all-concrete, all-timber), one on top of the other. For example, a Steel Over Concrete indicates an all-steel structural system located on top of an all-concrete structural system, with the opposite true of Concrete Over Steel.
Composite
A combination of materials (e.g. steel, concrete, timber) are used together in the main structural elements. Examples include buildings which utilize: steel columns with a floor system of reinforced concrete beams; a steel frame system with a concrete core; concrete-encased steel columns; concrete-filled steel tubes; etc. Where known, the CTBUH database breaks out the materials used within a composite building’s primary structural elements.
Composite
Official Website
Height
117.6 m / 386 ft
Floors Above Ground
35
# of Hotel Rooms
299
# of Elevators
6
Top Elevator Speed
3.5 m/s
Tower GFA
23,184 m² / 249,550 ft²
Rankings
-
By function
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
-
By material
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Construction Schedule
Proposed
Construction Start
Completed
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Owner/Developer
Call Tower Invest AB
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Wingardh Arkitektkontor
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Integra Engineering AB
MEP Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
AB Teknoplan
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
CTBUH Awards & Distinctions
Best Tall Building, by Region, Europe 2012 Award of Excellence
2012 CTBUH Awards
About Victoria Tower
Victoria Tower stands out among its neighbors and acts as an icon for the surrounding area. Situated between Stockholm proper and the city airport, the hotel and office tower serves the area with conference and office facilities, as well as providing a 299-room hotel. Seen on the way into the city, the tower stands out as a welcoming figure along the expressway.
Sited in Kista Science City, the hotel serves a mixed population of researchers, students, and businessmen. Nearby are the Kista Expo Center and shopping center, as well as other amenities. Just 15 minutes away from the Stockholm city center and 20 minutes away from the nearest airport, the tower’s location is ideal.
Within the tower, a mix of programs acts to meet the needs of the diverse range of users. An open approach to the lobby, lounge, and restaurant creates a large space conducive to meeting or relaxing, as well as serving the basic needs of meal service and guest reception. The skybar on the 34th floor offers views of both the surrounding environs as well as Stockholm in the distance.
The tower has a parallelogram-shaped plan for floors 2–21, which comprises the hotel rooms, while the upper floors are rectangular, delineating the office spaces. The top floors cantilever over the main form of the building, emphasizing its geometry. At 34 floors, the tower is a simple yet highly delineated prismatic tower in both its form and materiality.
The tesselated façade of the building is clad entirely in colored glass, though in actuality two-thirds of the walls are fully insulated. This allows the tower to appear as a prism in its geometry and materiality while meeting the needs for energy conservation. Software was developed specifically for the project to create a randomized yet uniform appearance. Due to the nature of the reflective and colorful glazing, the experience of the building changes with the viewer’s perspective. Changes in daylight, weather, and season also affect the expression of the façade, ultimately creating a new and different representation for every visitor.
The triangulated module of the façade is heavily articulated on the inside of the building, with a seemingly random mix of solid versus transparent modules. This pattern brings in daylight in a very non-traditional way, as opposed to typical rectangular window openings. At night, the glow on the exterior of the building is the opposite of this effect; brightly lit triangles are interspersed with solid walls, further emphasizing the geometric expression of the tower.
Relying on Scandinavian Modernism with a mix of color and classic designers, the interiors of the building are light and clean. Furnishings by Vitra are found throughout, along with classic Scandinavian light hardwoods and white wall treatments.
As the second tallest building in Stockholm, Victoria Tower sets a unique precedent for the approach to building tall in a typically low-rise region. The straightforward formal geometry and highly developed textural façade treatment are a modern interpretation of traditional Scandinavian approaches: simple yet extremely well-executed.
CTBUH Awards & Distinctions
Best Tall Building, by Region, Europe 2012 Award of Excellence
2012 CTBUH Awards
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy


















