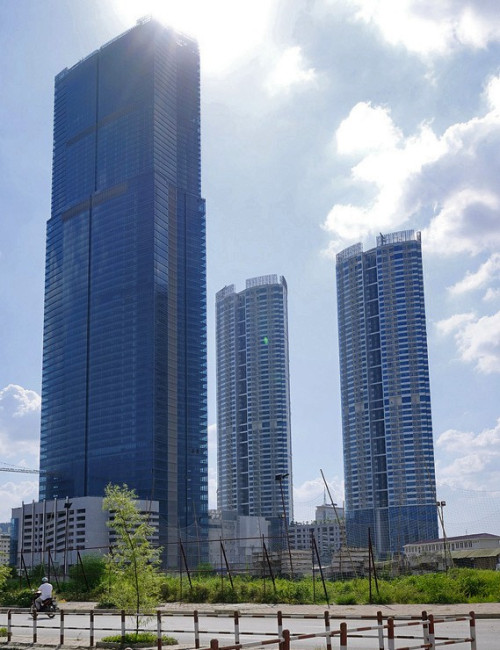
Keangnam Hanoi
Hanoi
- CTBUH Drawing
- Facts
-
Metrics
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
To Tip:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest point of the building, irrespective of material or function of the highest element (i.e., including antennae, flagpoles, signage and other functional-technical equipment).Architectural:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the architectural top of the building, including spires, but not including antennae, signage, flag poles or other functional-technical equipment. This measurement is the most widely utilized and is employed to define the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat (CTBUH) rankings of the "World's Tallest Buildings."Occupied:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest occupied floor within the building.
Above Ground
The number of floors above ground should include the ground floor level and be the number of main floors above ground, including any significant mezzanine floors and major mechanical plant floors. Mechanical mezzanines should not be included if they have a significantly smaller floor area than the major floors below. Similarly, mechanical penthouses or plant rooms protruding above the general roof area should not be counted. Note: CTBUH floor counts may differ from published accounts, as it is common in some regions of the world for certain floor levels not to be included (e.g., the level 4, 14, 24, etc. in Hong Kong).Below Ground
The number of floors below ground should include all major floors located below the ground floor level.Official Name
Keangnam Hanoi
Type
Complex
Status
Completed
Country
City
Function
hotel / office / residential
# of Apartments
300
# of Hotel Rooms
383
Map of Buildings in Complex
Note: Only buildings that have GPS coordinates recorded are displayed.
List of Buildings in Complex
|
RANK
|
Name
|
Completion
|
Height
|
Floors
|
Function
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Keangnam Hanoi Landmark Tower | 2012 |
329 m / 1,078 ft |
72 | Hotel / Residential / Office |
| 2 | Keangnam Hanoi Residential Tower 1 | 2011 |
212 m / 696 ft |
49 | Residential |
| 2 | Keangnam Hanoi Residential Tower 2 | 2011 |
212 m / 696 ft |
49 | Residential |
CTBUH Initiatives
CTBUH Releases Year in Review: Tall Trends of 2012
31 December 2012 - CTBUH Journal
Videos

03 March 2008
Sustainable Design in South Korea and Vietnam
Matthias A. Olt & James P. Rothwell of Callison, discussed two high-rise towers in South Korea and Vietnam at the CTBUH 8th World Congress in...
Research

01 September 2017
Application of Post-Tension Technology on Tall Buildings
Kwangryang Chung, Jungwoo Park & Younghye Kim, Dong Yang Structural Engineers Co., Ltd; Dohun Kim, POSCO E&C
It’s been a decade since post-tension system began to be applied in earnest to buildings in Korea. In the meantime, posttension system has been used...
Research

01 September 2017
Application of Post-Tension Technology on Tall Buildings
Kwangryang Chung, Jungwoo Park & Younghye Kim, Dong Yang Structural Engineers Co., Ltd; Dohun Kim, POSCO E&C
It’s been a decade since post-tension system began to be applied in earnest to buildings in Korea. In the meantime, posttension system has been used...

31 December 2012
Year in Review: Tall Trends of 2012
Kevin Brass, Antony Wood & Marty Carver, CTBUH
For the first time in six years the number of tall buildings completed annually around the world declined as the effects of the global financial...





