Filter by
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
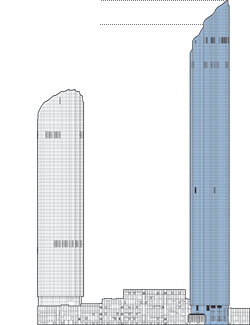
Burj Mohammed Bin Rashid
World Trade Center Abu Dhabi - The Residences
Building
Completed
2014
Residential
All-Concrete
381.2 m / 1,251 ft
88
5
474
13
7 m/s
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Proposed
Construction Start
Completed
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The CTBUH lists a project manager when a specific firm has been commissioned to oversee this aspect of a tall building’s design/construction. When the project management efforts are handled by the developer, main contract, or architect, this field will be omitted.
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
These are firms that consult on the design of a building's façade. May often be referred to as "Cladding," "Envelope," "Exterior Wall," or "Curtain Wall" Consultant, however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Façade Consultant" exclusively.
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
2015 CTBUH Awards
28 November 2018 - CTBUH Research
13 October 2016 - CTBUH Research

12 November 2015 | Abu Dhabi
Yoram Eilon, Seinor Vice President, WSP | Parsons Brinckerhoff, Kenneth Lewis, Managing Partner, Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, Hin Kong Poon, Deputy Chief Development Officer, CapitaLand...

22 August 2022
S. Isaac Work & Shawn Ursini, Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat
Tall building design has diversified and adapted to accommodate increased demand for distinctive amenities at a range of heights. Swimming pools are a classic feature...
The Burj Mohammed Bin Rashid is located in the heart of Abu Dhabi at the site of the old Central Market, a traditional crossroads and meeting point in the city. The tower’s central location provides residents with easy access to major points of interest, including the nearby Mall at the World Trade Center and the Corniche, a waterfront promenade that runs along the coast. As part of the larger World Trade Center complex, Burj Mohammed Bin Rashid is just one element of a 700,000-square-meter mixed-use development, which also includes an office building and a hotel. The site also includes a traditional souk, up to seven levels of retail in the podium, a green roof above the market, and a bridge system linking these areas together.
The tower is intended to fit within its desert context. A smooth, sleek, and reflective façade is designed to require minimal amounts of maintenance in such a dusty environment. Meanwhile, layers of internal shading control glare and unwanted heat gain. The exterior envelope of the tower undulates in waves as it wraps around the core. This glass cladding creates a mirage effect that alludes to its geographic context. The billowing design generates unique floor plans that deviate widely from those found in a typical tall building, resulting in an assortment of multiform spaces.
A number of design elements have been integrated into the building in order to increase its energy efficiency, including solar collectors and a ventilated three-skin façade. Additionally, local building materials were used wherever possible during construction to reduce the economic and environmental costs of transporting imported materials.
2015 CTBUH Awards

12 November 2015 | Abu Dhabi
Yoram Eilon, Seinor Vice President, WSP | Parsons Brinckerhoff, Kenneth Lewis, Managing Partner, Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, Hin Kong Poon, Deputy Chief Development Officer, CapitaLand...

12 November 2015 | Abu Dhabi
Toby Blunt, Partner, Foster + Partners, and Robert Halvorson, Executive Vice President, Halvorson and Partners, speak at the 14th Annual Best Tall Building Symposium in...

12 November 2015 | Abu Dhabi
Toby Blunt, Partner, Foster + Partners, & Robert Halvorson, Principal, Halvorson and Partners, are interviewed by Chris Bentley regarding the 2015 CTBUH Best Tall Building...

22 August 2022
S. Isaac Work & Shawn Ursini, Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat
Tall building design has diversified and adapted to accommodate increased demand for distinctive amenities at a range of heights. Swimming pools are a classic feature...
20 October 2018
CTBUH Research
The Middle East region is hosting its first CTBUH International Conference since 2008. In that year, there were 119 completed buildings of 150 meters or...
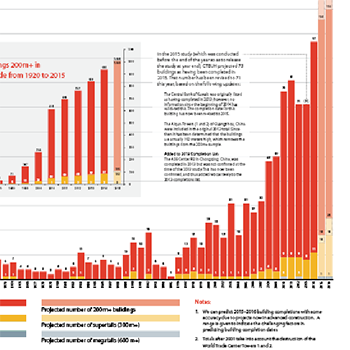
31 December 2014
Daniel Safarik, Antony Wood, Marty Carver & Marshall Gerometta, CTBUH
An All-Time Record 97 Buildings of 200 Meters or Higher Completed in 2014 and 2014 showed further shifts towards Asia, and also surprising developments in...

14 November 2013
CTBUH Research
Twenty years ago, the Middle East contained only one skyscraper over 150 meters in height. It is now estimated that by the end of 2015...
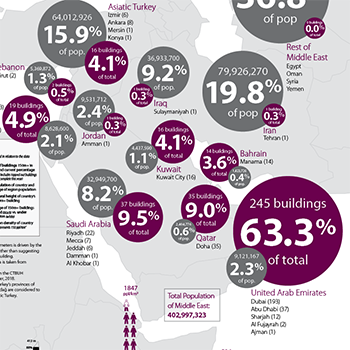
28 November 2018
CTBUH has released a Tall Buildings in Numbers (TBIN) interactive data study examining the relationship between high-rise growth and population in the Middle East.
13 October 2016
The Council is pleased to announce the Top Company Rankings for numerous disciplines as derived from the list of projects appearing in 100 of the World’s Tallest Buildings.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy