Filter by
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Menara TM
Bamboo Tower, Telekom Malaysia Headquarters, Menara Telekom
Building
Completed
2001
Office
All-Concrete
310 m / 1,017 ft
55
3
148,643 m² / 1,599,980 ft²
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Construction Start
Completed
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
The main contractor is the supervisory contractor of all construction work on a project, management of sub-contractors and vendors, etc. May be referred to as "Construction Manager," however, for consistency CTBUH uses the term "Main Contractor" exclusively.
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
31 July 2019 - Event
19 April 2007 - Event

01 August 2020
Antony Wood, Peng Du & Daniel Safarik, CTBUH
For more than a century, architects and urban visionaries have foretold of three-dimensional cities, with tall buildings linked by skybridges forming a new kind of...
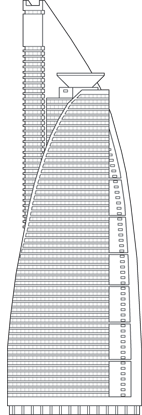
Located on the eastern edge of the Kuala Lumpur city limits, the Menara TM is the tallest building within an outlying cluster of high-rises built alongside a juncture of expressways and rail lines. The design was envisioned as a plant springing from the ground to reach light with an unfurling leaf.
Menara TM is perched upon a long horizontal base spreading across the block and extending 3 stories underground. The tower then rises with a central core and two offset office curving office wings. The wings create open courtyards flanking each side of the tower core which support a series of 11 outdoor terraces facing to the southeast and the northwest. As one office wing tops out, a helipad takes over the set back with a large disc shaped cantilever extending outward from the roofline. The second office wing then continues upward to not only crown the building with a distinctive shape, but also to support signage for Menara Telekom who commissioned the building to serve as their corporate headquarters.

01 August 2020
Antony Wood, Peng Du & Daniel Safarik, CTBUH
For more than a century, architects and urban visionaries have foretold of three-dimensional cities, with tall buildings linked by skybridges forming a new kind of...

11 June 2014
CTBUH Research
In this installment of Tall Buildings in Numbers, CTBUH considers how helipads are used on skyscrapers, and which are the highest in the world. The...
31 July 2019
Three researchers from the CTBUH Skybridges Research Team visited four key skybridge-linked projects in Shenzhen, Chongqing, Beijing, and Kuala Lumpur.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy