Height rank
Nina Tower
Hong Kong
- CTBUH Drawing
- Facts
-
Metrics
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
To Tip:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest point of the building, irrespective of material or function of the highest element (i.e., including antennae, flagpoles, signage and other functional-technical equipment).Architectural:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the architectural top of the building, including spires, but not including antennae, signage, flag poles or other functional-technical equipment. This measurement is the most widely utilized and is employed to define the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat (CTBUH) rankings of the "World's Tallest Buildings."Occupied:
Height is measured from the level of the lowest, significant, open-air, pedestrian entrance to the highest occupied floor within the building.Above Ground
The number of floors above ground should include the ground floor level and be the number of main floors above ground, including any significant mezzanine floors and major mechanical plant floors. Mechanical mezzanines should not be included if they have a significantly smaller floor area than the major floors below. Similarly, mechanical penthouses or plant rooms protruding above the general roof area should not be counted. Note: CTBUH floor counts may differ from published accounts, as it is common in some regions of the world for certain floor levels not to be included (e.g., the level 4, 14, 24, etc. in Hong Kong).Below Ground
The number of floors below ground should include all major floors located below the ground floor level.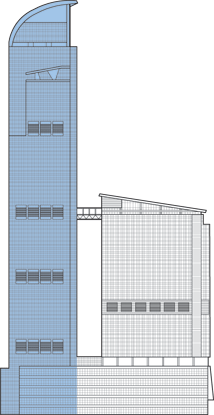
Official Name
Nina Tower
Other Names
Teddy Tower, Nina Tower I
Name of Complex
Type
Building
Status
Completed
Completion
2006
Country
City
Address
Function
A mixed-use tall building contains two or more functions (or uses), where each of the functions occupy a significant proportion of the tower's total space. Support areas such as car parks and mechanical plant space do not constitute mixed-use functions. Functions are denoted on CTBUH "Tallest Building" lists in descending order, e.g., "hotel/office" indicates hotel function above office function.
Hotel / Office
Structural Material
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from steel. Note that a building of steel construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of steel beams is still considered an “all-steel” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
All-Concrete
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from concrete which has been cast in place and utilizes steel reinforcement bars and/or steel reinforced concrete which has been precast as individual components and assembled together on-site.
All-Timber
Both the main vertical/lateral structural elements and the floor spanning systems are constructed from timber. An all-timber structure may include the use of localized non-timber connections between timber elements. Note that a building of timber construction with a floor system of concrete planks or concrete slab on top of timber beams is still considered an “all-timber” structure as the concrete elements are not acting as the primary structure.
Mixed-Structure
Utilizes distinct systems (e.g. all-steel, all-concrete, all-timber), one on top of the other. For example, a Steel Over Concrete indicates an all-steel structural system located on top of an all-concrete structural system, with the opposite true of Concrete Over Steel.
Composite
A combination of materials (e.g. steel, concrete, timber) are used together in the main structural elements. Examples include buildings which utilize: steel columns with a floor system of reinforced concrete beams; a steel frame system with a concrete core; concrete-encased steel columns; concrete-filled steel tubes; etc. Where known, the CTBUH database breaks out the materials used within a composite building’s primary structural elements.
All-Concrete
Height
320.4 m / 1,051 ft
Floors Above Ground
80
Floors Below Ground
2
Rankings
-
By function
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
-
By material
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Construction Schedule
Proposed
Construction Start
Completed
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
MEP Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Other Consultant
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
You must be a CTBUH Member to view this resource.
Developer
Chinachem Group
Architect
Usually involved in the front end design, with a "typical" condition being that of a leadership role through either Schematic Design or Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Arthur CS Kwok; Casa Design International; Dennis Lau & Ng Chun Man Architects & Engineers (HK) Ltd. (DLN)
Structural Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
MEP Engineer
The Design Engineer is usually involved in the front end design, typically taking the leadership role in the Schematic Design and Design Development, and then a monitoring role through the CD and CA phases.
Other Consultant
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Other Consultant refers to other organizations which provided significant consultation services for a building project (e.g. wind consultants, environmental consultants, fire and life safety consultants, etc).
Material Supplier
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Material Supplier refers to organizations which supplied significant systems/materials for a building project (e.g. elevator suppliers, facade suppliers, etc).
Toshiba Elevator and Building Systems Corporation (TELC)
Videos

20 October 2016 | Hong Kong
Skyscrapers in Hong Kong
Thursday October 20, 2016. Hong Kong, China. Eric Ma of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region presents at the 2016 China Conference Plenary 6: Hong Kong...
Research

31 December 2006
Tallest Buildings Completed in 2006
Nina Tower 1 in Hong Kong, at 319 meters high, leads the list of the ten tallest buildings completed in 2006. The Sports City Tower/Aspire...
About Nina Tower
The Nina Tower Development consists of two towers. The taller of the two buildings, is nicknamed Teddy Tower, was originally intended to stand 200 meters (656 feet) higher than it does currently and would have been the tallest building in the world at the time of concept planning. However, the height was restricted by the Government due to the proximity of the tower to the nearby Chek Lap Kok Airport.
To stand against strong typhoons in Hong Kong, the Nina Tower is stabilized by two levels of steel outriggers. It acts together with a reinforced concrete core wall and perimeter composite columns. A post-tensioned concrete flat slab with perimeter beam makes up the floor structure. Tailor-made table system formwork for the floor, and climb form for the core wall were used and thus sped up the construction cycle.
A shopping mall and exhibition spaces occupy the lower stories of the development, which is topped by 30 stories of offices in the Nina Tower. The smaller tower (dubbed L`Hotel Nina Tower) and the top 40 stories of the Nina Tower house a five-star hotel. The two towers are connected by a Skybridge at the top of the shorter building. The Skybridge linking the two towers is curved in plan and the struc-ture comprises two 3-meter (10-foot)-deep triangular space trusses.
The Nina Tower Development plays an essential role in continuing to bring Hong Kong into a new era of modern architecture and development. It also serves to provide an exciting, state of the art destination for visitors and at the same time offers a magnificent office and hotel facility for local businesses.
Subscribe below to receive periodic updates from CTBUH on the latest Tall Building and Urban news and CTBUH initiatives, including our monthly newsletter. Fields with a red asterisk (*) next to them are required.
View our privacy policy












